Overview of MPLS Forwarding

Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) is a kind of IP (Internet Protocol) backbone network technology. MPLS introduces the concept of connection-oriented label switching on a connectionless IP network, and combines Layer 3 routing technology with Layer 2 switching technology to give full play to the flexibility of IP routing and the simplicity of Layer 2 switching.
MPLS originated from IPv4 (Internet Protocol version 4), and its core technology can be extended to multiple network protocols, including IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6), IPX (Internet Packet Exchange), and CLNP (Connectionless Network Protocol). "Multiprotocol" in MPLS refers to support for multiple network protocols.
This shows that MPLS is not a service or application, it is actually a tunneling technology. This technology not only supports multiple high-level protocols and services, but also guarantees the security of information transmission to a certain extent.
MPLS label forwarding table
Before forwarding the data packet, the MPLS network router generates the routing table RIB according to the routing protocol The router's hardware CEF will generate a FIB table for hardware forwarding (this table is similar to a routing table). Then the router will generate the label database LIB table through the LDP protocol, Then the LDP protocol will generate the label forwarding table LFIB based on the LIB table and the original FIB table
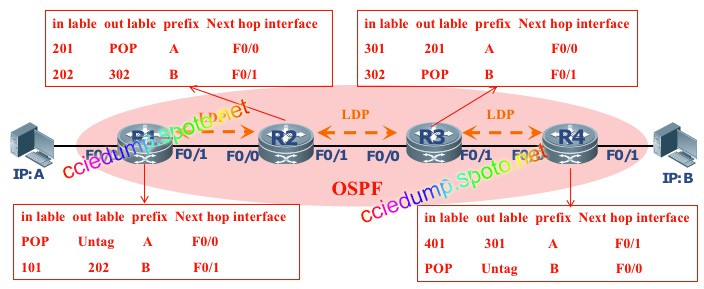
The label forwarding table records information such as incoming labels, outgoing labels, operations performed on labels, and outgoing interfaces. In an MPLS network, packets are forwarded according to matching label forwarding entries.
The LDP protocol is a label distribution protocol and must be used in conjunction with the IGP protocol. Only when the network is reachable can LDP neighbors be established.
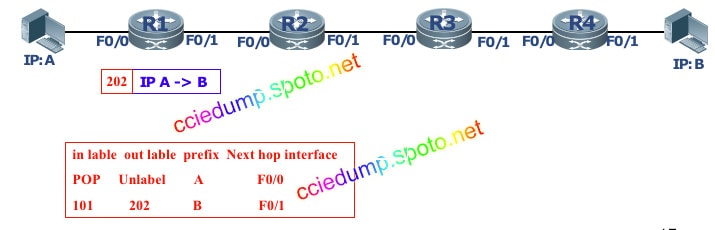
Ingress (R1) receives an unlabeled packet, determines the FEC to which the packet belongs and the corresponding label forwarding entry according to the destination address, and adds a label to the packet (202)
And forward the labeled packet from the corresponding outgoing interface (F0 / 1) to the next-hop LSR (R2).
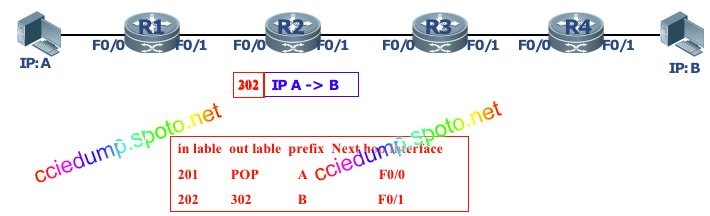
Router 2 looks up the label forwarding entry corresponding to the incoming label according to the label (202) on the packet.
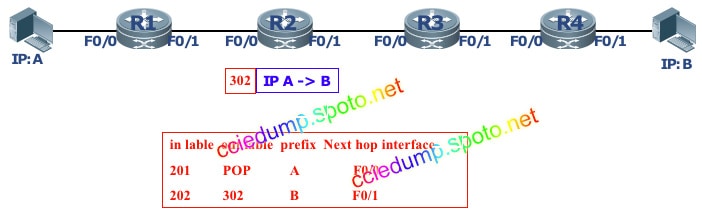
Replace the original label with a new label (302) and forward the labeled packet to the next-hop LSR (R3) from the corresponding outgoing interface (F0 / 1).
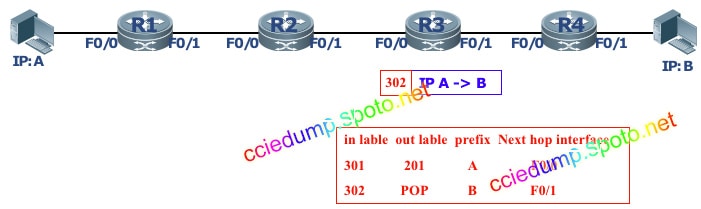
R3 finds the label forwarding entry corresponding to the incoming label according to the label (302) on the packet, and finds that it is a POP label, and the POp label is a pop-up action. We find that the label performs a label pop-up action in the penultimate hop of the mpls field
R4 looks up the routing table and forwards the packet from the corresponding interface
Forward the packet according to the IP header.
What is the penultimate popup?
IP lookup and label lookup:
If the LSR receives an IP packet, it looks at the FIB table, then the LSR pushes the IP packet into a label header, labels it with 16, and then forwards it from the F0 / 0 interface.
In CISCO, CEF switching is an IP forwarding mode used to mark packets, so CEF must be turned on on the router when MPLS is enabled.
When a router receives a labeled message, it searches in the LFIB table. The relevant matching entries in the LFIB table will have the outbound action or label for the inbound label and the next hop information.
If the router receives a labeled packet and the top label cannot be found in the local LFIB, then CISCO IOS will discard it
What is the impact if the penultimate popup is not performed?
The first search: after receiving the labeled packet, search the label forwarding table
The second search: After popping the label in the packet, the next layer of label forwarding or IP forwarding
Therefore, the Egress node should search the forwarding table twice before forwarding the packet: twice the label forwarding table or once the label forwarding table and once the routing forwarding table.
This increases the processing pressure of the edge device
Therefore, in order to reduce the burden on the egress node and improve the packet processing capability of the MPLS network, PHP can be used to pop the penultimate hop, and the label can be popped at the penultimate hop node. Egress implements the penultimate hop pop by assigning an empty label. The tag value of an empty tag is 3, and this value will not appear in the tag stack.
When an LSR finds that the label advertised by the downstream LSR is an empty label, it will directly pop the label and forward the packet to the downstream LSR (ie Egress). After Egress receives the packet, it directly forwards to the next layer. about cisco certification lookup click there
Summary of label processing actions
Remove:
The top label is removed. Packet forwarding relies on the remaining labels in the label stack or forwards them as unlabeled packets.
exchange:
The top label is removed, and a new label is used to replace the removed label.
Add to:
The top label is replaced (swapped) by a new label, and one or more labels are added above the replaced label.
Unlabeled / unlabeled:
The label stack is completely removed, and the packet is forwarded in an unlabeled manner.
polymerization:
The label stack is removed, and IP lookup is performed on the IP packet
What is the difference between POP and Untag?
POP
POP will only pop the top-level label header. The packet forwarded by this action can be an IP packet or an MPLS label packet. Untag will remove all label headers and turn it into a pure IP packet. .
The POP receives the empty label assigned to a specific prefix from the downstream. The value of this label is 3, then when the LSR sends data to the prefix to the downstream LSR, he will pop up the top-level label (POP) for forwarding , Note that this time only needs to check for this LSR
Find the LFIB once, there is information about the next hop in the LFIB, so the top-level label is popped up and then handed over to the next hop instead of looking up the FIB table again (if the label is an IP packet).
UNTAG
All labels are popped up and then forwarded according to the next hop (find FIB table). There are three reasons for untags:
No labels can be assigned downstream, MPLS is not enabled
The downstream label was divided but could not be transmitted because the LDP Neighbor was not established
The label assignment is incorrect. This situation occurs only when IGP is OSPF, because if the loopback port is used as the router-id of the ldp,
And it is not 32-bit, OSPF will automatically publish with a 32-bit loopback address, which will cause label assignment errors.