MPLS VPN Architecture-3
 The Solution to the Problem of Conflicts When Routing Is Transmitted in the Network Why do we need RD value? A very straightforward example of this problem is the technology you will encounter in the CCIE exam, and if you are not familiar with the principle of RD worth, and the configuration of the RD value in the exam is deleted by mistake, then you cannot pass CCIE (EI) LAB exam, because deleting an RD value will cause some configurations to be automatically deleted.
After successfully solving the problem of local routing conflicts, in the next step we need to resolve the conflicts of routing when passing through the network. Standard BGP can only handle IPv4 routing, so if different VPNs use the same IPv4 address prefix, the routing of different VPNs cannot be distinguished at the receiving end. Using the RT attribute can partially solve this problem, but it also has certain limitations. Let's analyze how to solve this problem and its limitations through RT.
■ After PE receives the routes from different VPNs, it decides which VRF the route enters according to the RT attribute, so as to ensure that the routes of different VPNs are not comparable and the operation can be carried out normally;
■ When the route is revoked, the BGP packet has no attributes, and RT certainly will not work, which will cause the same route in all VPNs to be revoked. Therefore, although RT has this function, it is not easy to use all the time. There must be a tag that can be bound to the IPv4 address to fundamentally solve this problem-we call this tag RD. RD is a mark attached to the front of the IPv4 address, and its format is shown in the figure:
The Solution to the Problem of Conflicts When Routing Is Transmitted in the Network Why do we need RD value? A very straightforward example of this problem is the technology you will encounter in the CCIE exam, and if you are not familiar with the principle of RD worth, and the configuration of the RD value in the exam is deleted by mistake, then you cannot pass CCIE (EI) LAB exam, because deleting an RD value will cause some configurations to be automatically deleted.
After successfully solving the problem of local routing conflicts, in the next step we need to resolve the conflicts of routing when passing through the network. Standard BGP can only handle IPv4 routing, so if different VPNs use the same IPv4 address prefix, the routing of different VPNs cannot be distinguished at the receiving end. Using the RT attribute can partially solve this problem, but it also has certain limitations. Let's analyze how to solve this problem and its limitations through RT.
■ After PE receives the routes from different VPNs, it decides which VRF the route enters according to the RT attribute, so as to ensure that the routes of different VPNs are not comparable and the operation can be carried out normally;
■ When the route is revoked, the BGP packet has no attributes, and RT certainly will not work, which will cause the same route in all VPNs to be revoked. Therefore, although RT has this function, it is not easy to use all the time. There must be a tag that can be bound to the IPv4 address to fundamentally solve this problem-we call this tag RD. RD is a mark attached to the front of the IPv4 address, and its format is shown in the figure: 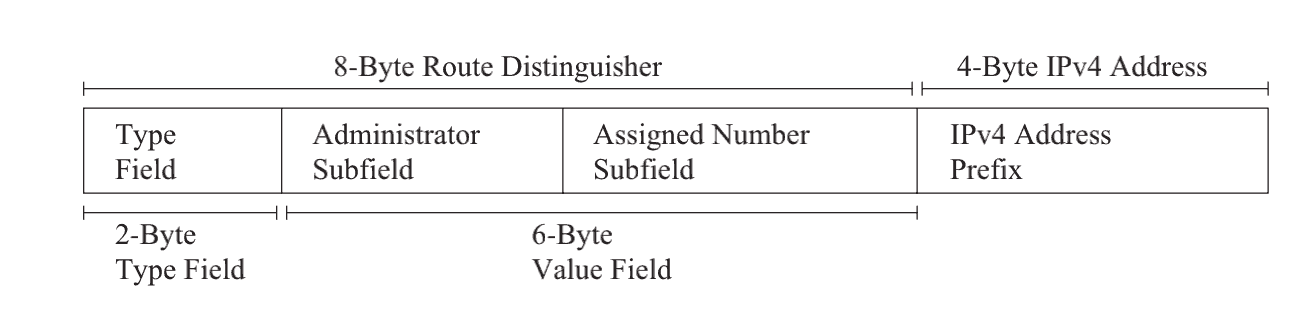 The type field defines two values: 0 and 1. For type 0, the manager sub-area includes 2 bytes, and the assigned value field includes 4 bytes. The manager sub-area uses an autonomous system number (ASN) to assign a value sub-area to the value space managed by the service provider. Type 0 cannot use private autonomous system numbers, which may cause conflicts. If you want to use a private autonomous system, you can use type 1. For Type 1, the manager sub-region includes 4 bytes, and the assigned value field includes 2 bytes. The manager sub-area uses IPv4 addresses and assigns value sub-areas to the value space managed by the service provider. The structure of RD is similar to RT, but they are essentially different.
RT is an extended attribute of BGP routing, and RD is appended to the IPv4 address and exists as part of the address. This needs everyone's attention. The characteristics of some applications of RD are as follows:
After adding RD to the IPv4 address, it becomes a VPN-IPv4 address family. In theory, it is possible to configure an RD for each VRF, but it must be guaranteed that this RD is unique globally. It is generally recommended to configure the same RD for each VPN. The VPN-IPv4 address is only used inside the service provider's network. It is added when the PE advertises the route, and it is placed in the local routing table after the PE receives the route to compare it with the route received later. The CE does not know that the VPN-IPv4 address is used. When it traverses the backbone of the provider, the VPN-IPv4 address is not carried in the packet header of the VPN data traffic. RD is only used when the backbone network routing protocol exchanges routes. And the standard route that the PE receives from the CE is an IPv4 route. If it needs to be advertised to other PE routers, an RD needs to be added to this route.
Because RD has these characteristics, if the same address exists in two VRFs, but the RD is different, then the two VRFs must not be able to visit each other, nor can indirect mutual visits. This is because the data packet does not carry RD when data is forwarded, so that when the data arrives at the destination, the PE will find the route entry to the same destination in different VRFs, resulting in incorrect forwarding. Although RD is carried in the process of routing and exchanging PE equipment, RD does not affect the routing between different VRFs and the formation of VPN. These things are handled by RT. The difference between RD and RT Features of RD In principle, the role of RD is to change the IPv4 address into a globally unique VPNv4 address. When overlapping IPv4 addresses appear in different VPNs, RD can distinguish them. The format used is usually ASN: N, and some are based on IP address formats, such as X.X.X.X: N, but the latter is not commonly used. So as long as the VPN addresses do not overlap, RD can be arbitrarily matched. According to the characteristics of the network, we use the ASN: N method and use this AS number + N (N can be arbitrarily valued). It is generally more common to use the same RD in the same VPN.
The type field defines two values: 0 and 1. For type 0, the manager sub-area includes 2 bytes, and the assigned value field includes 4 bytes. The manager sub-area uses an autonomous system number (ASN) to assign a value sub-area to the value space managed by the service provider. Type 0 cannot use private autonomous system numbers, which may cause conflicts. If you want to use a private autonomous system, you can use type 1. For Type 1, the manager sub-region includes 4 bytes, and the assigned value field includes 2 bytes. The manager sub-area uses IPv4 addresses and assigns value sub-areas to the value space managed by the service provider. The structure of RD is similar to RT, but they are essentially different.
RT is an extended attribute of BGP routing, and RD is appended to the IPv4 address and exists as part of the address. This needs everyone's attention. The characteristics of some applications of RD are as follows:
After adding RD to the IPv4 address, it becomes a VPN-IPv4 address family. In theory, it is possible to configure an RD for each VRF, but it must be guaranteed that this RD is unique globally. It is generally recommended to configure the same RD for each VPN. The VPN-IPv4 address is only used inside the service provider's network. It is added when the PE advertises the route, and it is placed in the local routing table after the PE receives the route to compare it with the route received later. The CE does not know that the VPN-IPv4 address is used. When it traverses the backbone of the provider, the VPN-IPv4 address is not carried in the packet header of the VPN data traffic. RD is only used when the backbone network routing protocol exchanges routes. And the standard route that the PE receives from the CE is an IPv4 route. If it needs to be advertised to other PE routers, an RD needs to be added to this route.
Because RD has these characteristics, if the same address exists in two VRFs, but the RD is different, then the two VRFs must not be able to visit each other, nor can indirect mutual visits. This is because the data packet does not carry RD when data is forwarded, so that when the data arrives at the destination, the PE will find the route entry to the same destination in different VRFs, resulting in incorrect forwarding. Although RD is carried in the process of routing and exchanging PE equipment, RD does not affect the routing between different VRFs and the formation of VPN. These things are handled by RT. The difference between RD and RT Features of RD In principle, the role of RD is to change the IPv4 address into a globally unique VPNv4 address. When overlapping IPv4 addresses appear in different VPNs, RD can distinguish them. The format used is usually ASN: N, and some are based on IP address formats, such as X.X.X.X: N, but the latter is not commonly used. So as long as the VPN addresses do not overlap, RD can be arbitrarily matched. According to the characteristics of the network, we use the ASN: N method and use this AS number + N (N can be arbitrarily valued). It is generally more common to use the same RD in the same VPN.
| VPN-sale | ASN :100 |
| VPN-fifinance | ASN :200 |
| VPN-manage | ASN :300 |
| ASN is the AS number |
| VPN-sale | export=ASN :100 | import=ASN :100 |
| VPN-fifinance | export=ASN :200 | import=ASN :200 |
| VPN-manage | export=ASN :300 | import=ASN :300 |
Related Articles:
1. MPLS VPN Architecture-1
Recommended Reading: