Cisco Basic Knowledge: What Is Overlay?
 Three problems with traditional networks
The scope of virtual machine migration is limited by the network architecture
Due to the network attribute requirements of virtual machine migration, if it is migrated from one physical machine to another physical machine and requires uninterrupted service of the virtual machine, its IP address, MAC address and other parameter dimensions need to remain unchanged. Layer 2 network, and requires the network itself to have the redundancy and reliability of multipath and multilink.
Virtual machine size is limited by network specifications
In the large layer 2 network environment, the data flow needs to pass through explicit network addressing to ensure that it reaches the destination accurately. Therefore, the size of the layer 2 address table entry (MAC address table) of the network device has become the virtual machine in the cloud computing environment The upper limit of the scale.
Network isolation / separation capability limitation
The current mainstream network isolation technology is VLAN (or VPN), and there will be problems in the deployment of large-scale virtualized environments. The number of VLANs is only 12 bit units in the standard definition, and the available number is about 4,000. Such an order of magnitude is for public Cloud or large virtualized cloud computing applications are trivial. Based on this driving force, Overlay's virtualized network technology trend has evolved gradually.
Three problems with traditional networks
The scope of virtual machine migration is limited by the network architecture
Due to the network attribute requirements of virtual machine migration, if it is migrated from one physical machine to another physical machine and requires uninterrupted service of the virtual machine, its IP address, MAC address and other parameter dimensions need to remain unchanged. Layer 2 network, and requires the network itself to have the redundancy and reliability of multipath and multilink.
Virtual machine size is limited by network specifications
In the large layer 2 network environment, the data flow needs to pass through explicit network addressing to ensure that it reaches the destination accurately. Therefore, the size of the layer 2 address table entry (MAC address table) of the network device has become the virtual machine in the cloud computing environment The upper limit of the scale.
Network isolation / separation capability limitation
The current mainstream network isolation technology is VLAN (or VPN), and there will be problems in the deployment of large-scale virtualized environments. The number of VLANs is only 12 bit units in the standard definition, and the available number is about 4,000. Such an order of magnitude is for public Cloud or large virtualized cloud computing applications are trivial. Based on this driving force, Overlay's virtualized network technology trend has evolved gradually.
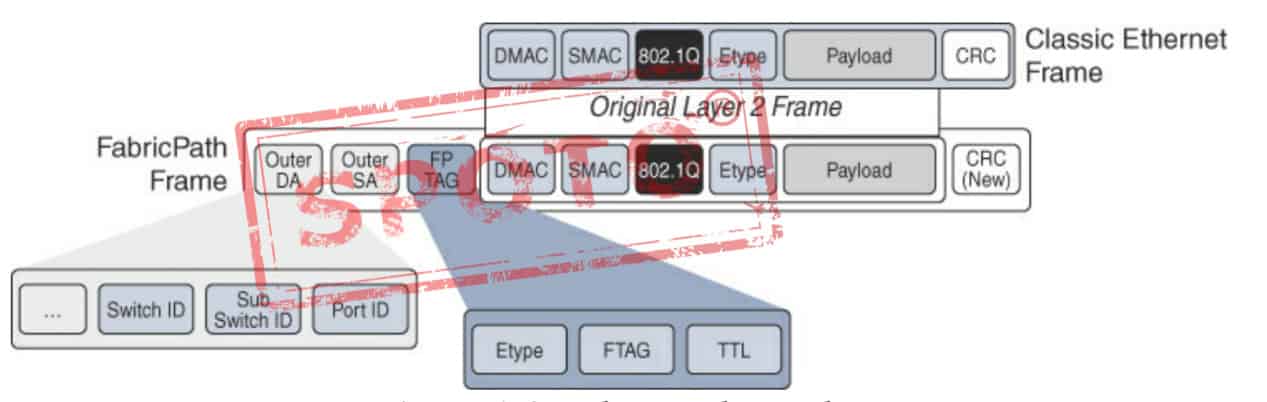
FabricPath Header
Introduction Overlay in the field of network technology refers to a virtualization technology mode superimposed on the network architecture. Its general framework is to implement the application of the network on the network without large-scale modification of the basic network and can be used with other networks The business is separated and based on the basic network technology based on IP. In fact, this model is formed by optimizing traditional technology. In response to the three major technical challenges presented above, Overlay provides a completely new solution.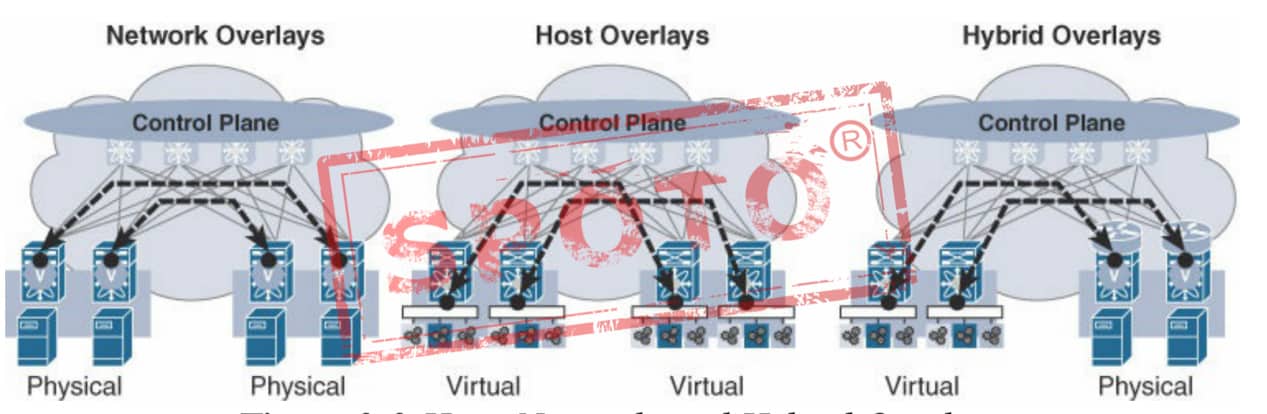
Host, Network, and Hybrid Overlays
Solution for the limitation of virtual machine migration scope limited by network architecture Overlay is a new data format encapsulated in IP packets. Therefore, this data can be distributed in the network by routing, and the routing network itself has no special network structure restrictions and has a benign large-scale scalability And there are no special requirements for the device itself, preferably with high-performance routing and forwarding, and the routing network itself has strong fault self-healing ability and load balancing ability. Solution for the limitation of virtual machine size limited by network specifications After the virtual machine data is encapsulated in the IP data packet, it only appears to the network as the encapsulated network parameters, that is, the address of the tunnel endpoint. Therefore, for the bearer network (especially the access switch), the MAC address specification requirements are greatly reduced The minimum specification is dozens (the tunnel endpoint MAC of a physical server per port). Solution to the limitation of network isolation / separation capability In view of the limitation of the number of VLANs within 4000, a user ID like 12-bit VLAN ID is introduced in Overlay technology, which supports user identification of more than 10 million levels, and the concept of cloud computing "tenant" is followed in Overlay, which is called Tenant ID (tenant identification), represented by 24 or 64 bits. In response to the problem of TRUENK ALL (VLAN penetrating all devices) of the network under VLAN technology, Overlay has no requirements for the VLAN configuration of the network, which can avoid the waste of invalid traffic bandwidth of the network itself. At the same time, Overlay's Layer 2 connectivity is created based on virtual machine business requirements. Globally controllable in a cloud environment.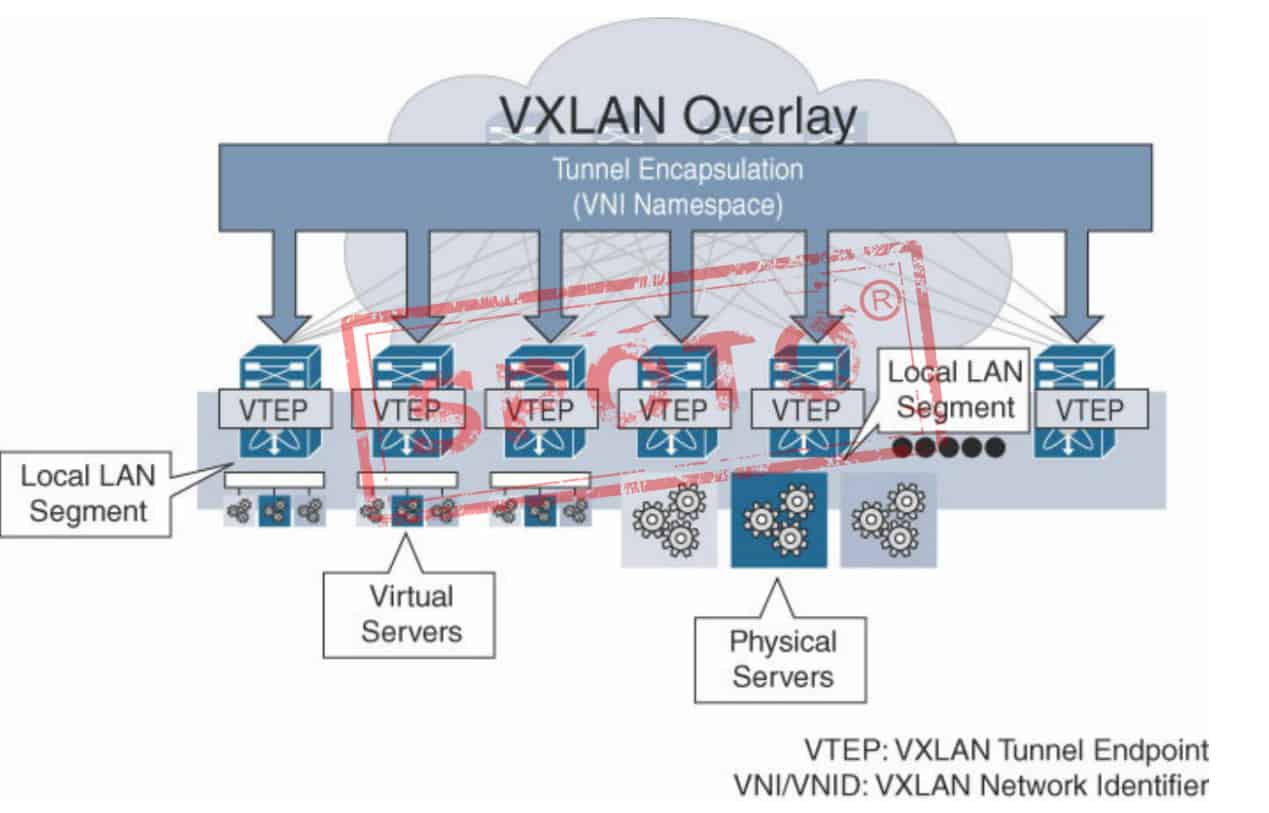
Overlay Taxonomy
Three main technologies of Overlay Currently, the IETF has the following three major technical routes in the Overlay technology field. For simplicity, this article only discusses IPv4-based Overlay-related content. VXLAN VXLAN is a tunnel forwarding mode in which Ethernet packets are encapsulated on the UDP transport layer. The destination UDP port number is 4798; IP, Layer 4 port number, etc.) HASH value is used as UDP number; uses 24 bits to identify the layer 2 network segment, called VNI (VXLAN Network Identifier), similar to the role of VLAN ID; unknown purpose, broadcast, multicast and other networks Traffic is encapsulated as multicast forwarding, and the physical network is required to support any source multicast (ASM). NVGRE The main supporter of NVGRE is Microsoft. Unlike VXLAN, NVGRE does not use the standard transmission protocol (TCP / UDP), but uses the General Routing Encapsulation Protocol (GRE). NVGRE uses the lower 24 bits of the GRE header as the tenant network identifier (TNI) and can support 1,600 virtual networks like VXLAN. In order to provide a stream that describes the granularity of bandwidth utilization, the transmission network needs to use GRE headers, but this causes NVGRE to be incompatible with traditional load balancing. This is the biggest difference between NVGRE and VXLAN. To improve load balancing capabilities, it is recommended that each NVGRE host use multiple IP addresses to ensure that more traffic can be load balanced. NVGRE does not need to rely on flooding and IP multicast for learning, but broadcasts in a more flexible way, but this needs to rely on hardware / vendors. The last difference is about fragmentation. NVGRE supports reducing the maximum packet transmission unit to reduce the size of the internal virtual network packet, without requiring the transmission network to support the transmission of large frames. STT STT uses the data encapsulation form of TCP, but transforms the transmission mechanism of TCP. Data transmission does not follow the TCP state machine, but a newly defined stateless mechanism, redefines the meaning of each TCP field, and does not need three handshake to establish a TCP connection It is called stateless TCP; Ethernet data is encapsulated in stateless TCP; 64-bit Context ID is used to identify the layer 2 network segment; in order to make STT make full use of the balance of the network routing, the original Ethernet data header (MAC, IP , Layer 4 port number, etc.) as the source port number of stateless TCP; network traffic such as unknown destination, broadcast, and multicast are encapsulated as multicast forwarding. The general idea of these three Layer 2 Overlay technologies is to carry Ethernet packets to a certain tunnel level. The difference lies in the choice and construction of the tunnel, and the bottom layer is IP forwarding. The table above shows a comparison of the key features of these three technologies: VXLAN and STT have low requirements for traffic balancing on existing network devices, that is, load link load sharing has good adaptability. General network devices can perform link aggregation or equal-cost routing traffic balancing on L2-L4 data content parameters. NVGRE requires network devices to perceive GRE extension headers and HASH flow ID, which requires hardware upgrades; STT has a major modification to TCP, the tunnel mode is close to the UDP nature, the tunnel construction technology is innovative, and the complexity is relatively high, and VXLAN uses the existing general UDP transmission, and the maturity is extremely high. Overall, VLXAN technology has a comparative advantage.
Recommended Reading:
- Understanding the Costs, Benefits, and Pathways in Networking Certification Courses
- How Do I Study for Linux+ Certification?
- Unlocking the Path to Success: CCNP 300-410 ENARSI Exam Overview and Benefits
- CCIE Security V5.0 Lab Exam Review
- Elevate Your Career with CCNP Data Center: Insights into the 300-615 DCIT Exam