8 CMD Commands to Manage (Wireless) Networks in Windows

Table of Contents
- 1.PING
- Sample usage and output:
- 2.TRACERT
- Sample usage:
- 3.PATHPING
- Sample usage and output:
- 4.IPCONFIG
- Use this switch to flush your DNS cache:
- About SPOTO
As Windows users, control panels and Settings applications can feel their limited functionality. If you want to have full and absolute control over your network, which means accessing everything the operating system must provide, you will have to start using command prompts. Never used a command prompt? Don’t worry.Using it is as simple as typing the commands you’ll see below. It’s not hard. We’ll tell you everything you need to know at first. However, if you are still unsure, check out our command prompt beginner guide.
1.PING
Ping is one of the most basic but useful commands you might know. It tells you whether the computer can access a target IP address or domain name, or, if so, when the data is returned again.
Sample usage and output:
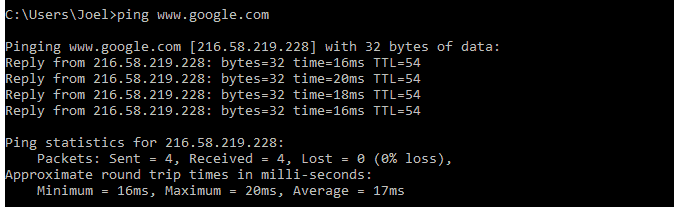
This command works by sending multiple packets and seeing how many of them are returned. If some of them don’t come back, it’ll tell you (lost). Packet loss leads to poor performance of games and streaming media, which is a good way to test.
By default it sends 4 packets, each one waiting 4 seconds before timing out. You can increase the number of packets like this:

And you can increase the timeout duration like this (value is in milliseconds)
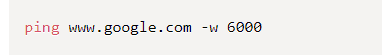
2.TRACERT
Tracert stands for Trace Route. Like ping, it sends packets as a solution to any network problems you may encounter, tracking the routing of packets when packets jump from the server to the server.
Sample usage:
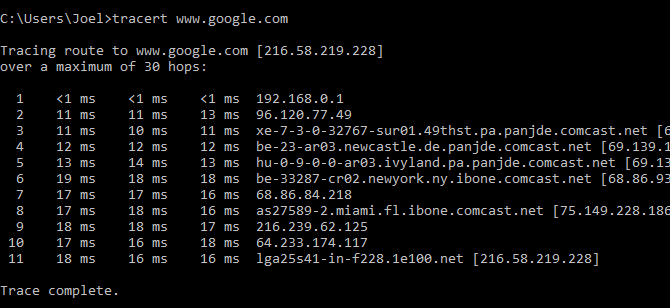
This command outputs a line-by-line summary of each hop, including the delay between you and the particular hop and the IP address of the hop (plus the domain name, if available).
Why do you see three delayed readings per jump? Because tracert sends three packets per hop in case one of them is lost or takes too much time without representing your real delay. The average of three is the best practice.
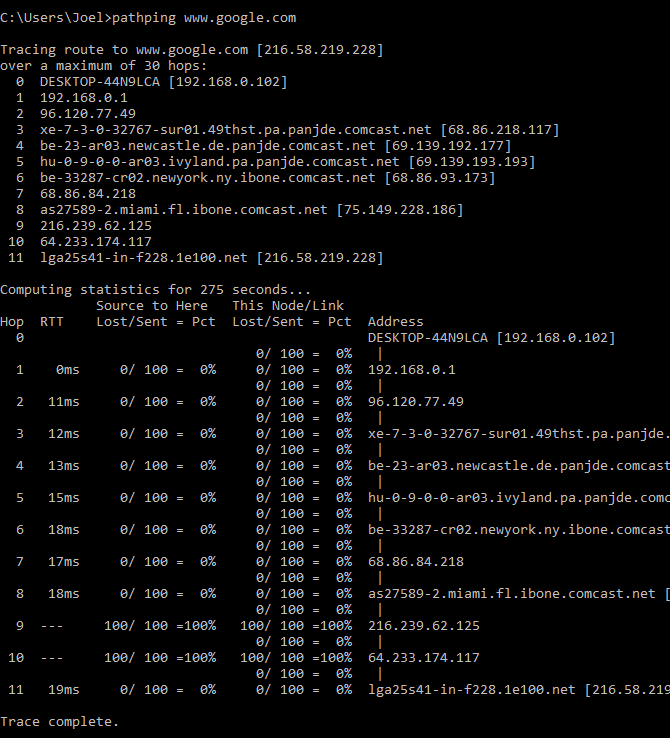
3.PATHPING
Pathping is similar to tracert, in addition to more information, which means that execution takes longer. After sending the packet to the specified destination, it analyzes the route used and calculates the packet loss by hops.
Sample usage and output:
4.IPCONFIG
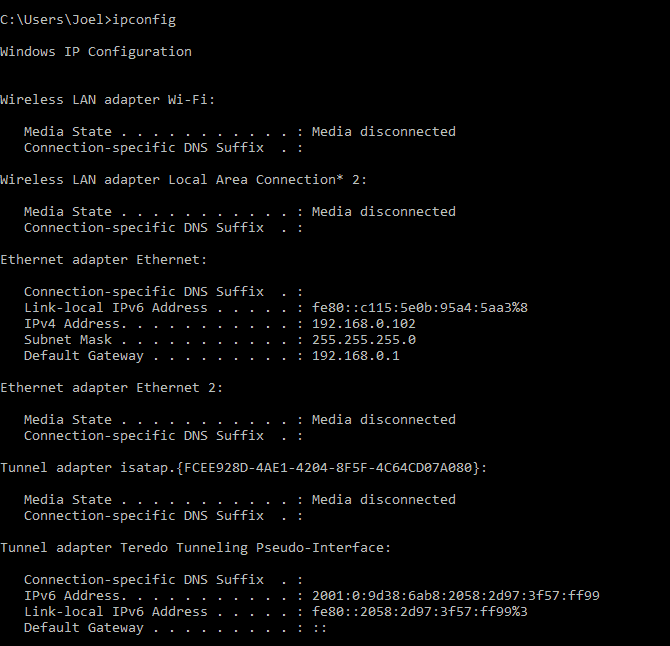
Ipconfig is probably just the most commonly used network command on Windows. It is not only useful for the information it provides, but also can be combined with several switches to perform certain tasks.
Sample usage and output:
The default output shows how each network adapter on the system and how they are resolved. The IPv4 address and default gateway details under the wireless LAN adapter and the Ethernet adapter section are the most important.
Use this switch to flush your DNS cache:
About SPOTO
SPOTO offers Cisco CCIE certification practice tests and training to help all candidates to pursue their ideal careers. You can also find more useful tips and suggestions to help you study and master the networking knowledge.
SPOTO has more study materials of CMD commands.If you want to get it and you can send an email: spoto@spotoclub.com we will send the study material to you